Understanding High Blood Sugar
What is High Blood Sugar?
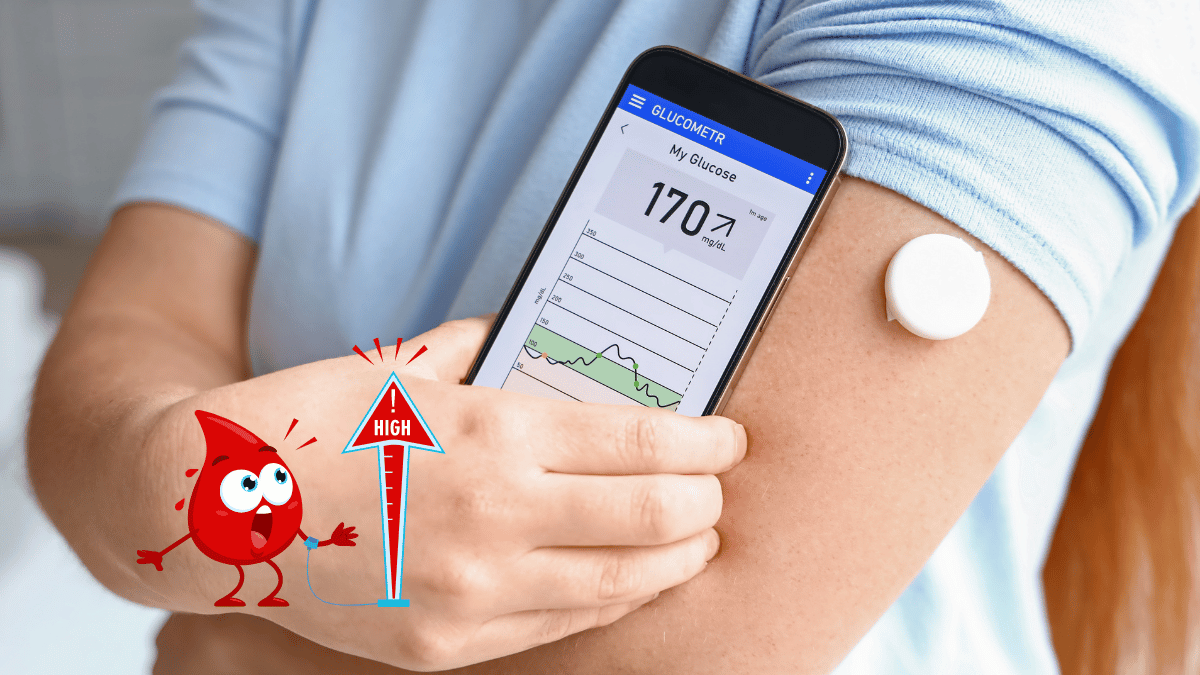
High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, occurs when the glucose levels in the bloodstream exceed normal levels. This condition is commonly associated with diabetes, but it can also arise from factors such as stress, illness, or dietary choices.
Typically, normal blood sugar levels range from 70 to 130 mg/dL before meals, and levels above this range indicate hyperglycemia.
Causes of High Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can contribute to elevated blood sugar levels. Diabetes is the most prevalent cause, particularly in cases of type 1 and type 2 diabetes, where the body struggles with insulin production or sensitivity. Dietary habits play a significant role as well; consuming foods high in carbohydrates or sugars can lead to spikes in blood sugar.
Physical inactivity can further exacerbate the issue by reducing insulin sensitivity. Stress, whether physical or emotional, can trigger the release of hormones that elevate blood sugar.
Additionally, illness or infection often prompts temporary increases in glucose levels, and certain medications, like corticosteroids, can also impact blood sugar control.
Symptoms and Risks of Untreated High Blood Sugar
The symptoms of high blood sugar can vary widely but commonly include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and headaches.
One potential outcome is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a life-threatening condition that can develop in individuals with type 1 diabetes. Chronic high blood sugar poses long-term risks, such as damage to blood vessels, which can result in cardiovascular issues, nerve damage, kidney problems, and vision loss.
Moreover, elevated glucose levels can impair the body’s ability to fend off infections, increasing susceptibility to illness. Managing high blood sugar is essential for preventing these symptoms and complications, making it crucial to be aware of its causes and signs for overall health maintenance.
Dietary Changes to Manage Blood Sugar
Foods to Include for Stable Blood Sugar
Incorporating the right foods into your diet is essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Focus on high-fiber foods such as whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables, as they help slow the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream.
Lean proteins, like chicken, fish, and plant-based options, can also support blood sugar control by promoting satiety and reducing cravings.
Healthy fats, found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil, play a role in maintaining energy levels and promoting overall health. Additionally, including low-glycemic index foods, which have a lesser impact on blood sugar levels, can be beneficial.
Foods to Avoid and Limit
Certain foods can lead to spikes in blood sugar and should be minimized or avoided. Sugary beverages, such as sodas and fruit juices, can cause rapid increases in glucose levels.
Refined carbohydrates, including white bread, pastries, and sugary snacks, can also contribute to unstable blood sugar. Processed foods high in trans fats and excessive sodium should be limited, as they may lead to long-term health issues.
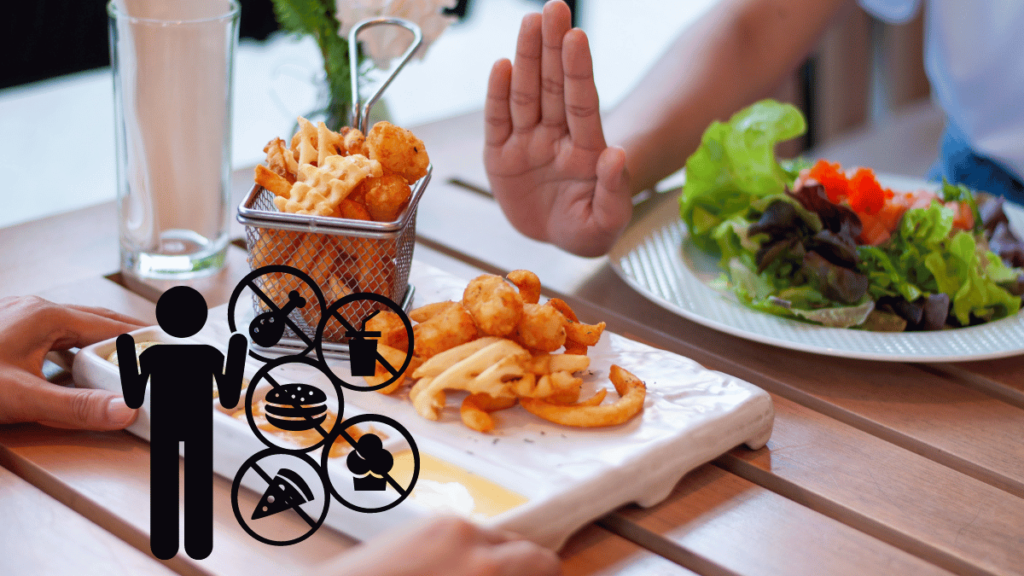

Instead of reaching for these options, it’s important to choose whole, nutrient-dense foods that promote better blood sugar control.
Importance of Portion Control
Portion control is really important for managing blood sugar levels. Even healthy foods can raise blood sugar if you eat too much of them. By being mindful of portion sizes, you can help control your calorie intake and avoid overeating.
Using smaller plates, measuring serving sizes, and being mindful of hunger cues can all aid in maintaining appropriate portions.
Balanced meals that combine carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in moderation can also support stable blood sugar levels. Developing a better understanding of portion sizes is essential for achieving long-term success in blood sugar management.
The Role of Exercise in Blood Sugar Management
Best Types of Exercise for Lowering Blood Sugar
Exercise plays a vital role in managing blood sugar levels, as it enhances insulin sensitivity and helps the body use glucose more effectively. Aerobic activities such as walking, running, swimming, and cycling are particularly effective for lowering blood sugar.
These exercises increase heart rate and promote calorie burning, contributing to overall metabolic health. Strength training is also beneficial; building muscle mass can improve glucose uptake and enhance insulin response.
Incorporating a mix of both aerobic and strength training exercises can provide optimal benefits for blood sugar management.
How Often Should You Exercise?
To effectively manage blood sugar levels, aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise each week, which can be broken down into manageable sessions throughout the week.
This might look like 30 minutes a day, five days a week. Strength training at least two days a week. Consistency is key; regular physical activity not only helps regulate blood sugar but also supports overall health and well-being.
Tips for Staying Active
Finding ways to stay active can make exercise more enjoyable and sustainable. Consider activities you genuinely enjoy, whether it’s dancing, hiking, or playing a sport, as this can motivate you to stick with a routine. Setting achievable goals and tracking your progress can also help maintain motivation.
Incorporate movement into your daily life by taking the stairs instead of the elevator, going for short walks during breaks, or engaging in active hobbies. Remember that even small amounts of physical activity can make a significant difference in blood sugar management.
Medication and Medical Support
When to Consider Medication
Medication may be necessary when lifestyle changes alone are insufficient to manage blood sugar levels. Individuals with type 1 diabetes typically require insulin therapy, while those with type 2 diabetes may need oral medications or insulin based on their specific needs.
If blood sugar remains consistently high despite dietary adjustments and exercise, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional to discuss medication options.
Working with Healthcare Professionals

Regular check-ups with your doctor can help monitor your condition and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
Endocrinologists, dietitians, and diabetes educators can provide valuable insights and support tailored to your individual needs.
Open communication about your lifestyle, challenges, and any symptoms you experience is vital for creating a comprehensive management plan.
Understanding Your Treatment Options
Understanding the various treatment options available is key to effective blood sugar management. This may include different types of insulin, oral medications, and other therapies designed to regulate blood sugar levels.
Each option has its benefits and potential side effects, so it’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to find the best approach for you. Staying informed about new treatments and advancements in diabetes care can also empower you to make informed decisions about your health.
Tips for Long-Term Success
Setting Realistic Goals
Setting realistic and achievable goals is essential for long-term success in managing blood sugar levels. Start with small, specific targets, such as making healthier food choices or gradually increasing physical activity.
These manageable goals can lead to significant improvements over time. Regularly reassessing and adjusting your goals based on your progress and lifestyle changes can help maintain motivation and ensure continued success.
Building a Support Network
Having a support network can make a significant difference in your journey to manage blood sugar effectively. Connecting with family, friends, or support groups can provide encouragement and accountability.
Sharing experiences with others facing similar challenges can offer valuable insights and foster a sense of community. Consider seeking out local or online support groups for individuals with diabetes to share tips, resources, and motivation.
Staying Informed and Educated
Staying informed about diabetes management and blood sugar control is vital for making empowered decisions about your health. Regularly consult reputable sources such as healthcare professionals, diabetes organizations, and educational materials to keep up with the latest research and strategies.
Knowledge about nutrition, exercise, and medication can enhance your ability to manage blood sugar levels effectively. Continuing education fosters confidence and encourages proactive management of your health.
Conclusion
Managing high blood sugar is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing serious complications. By understanding the factors that influence blood sugar levels, including diet, exercise, medication, and support systems, individuals can take proactive steps toward better management.
Implementing dietary changes, engaging in regular physical activity, and collaborating with healthcare professionals create a solid foundation for success. Setting realistic goals and building a supportive network further enhances this journey.
Staying informed and educated empowers individuals to make confident decisions about their health. With dedication and the right strategies, managing high blood sugar can lead to a healthier, more fulfilling life.
FAQ
What is high blood sugar?
High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, occurs when glucose levels in the bloodstream exceed normal limits.
What causes high blood sugar?
Common causes include diabetes, poor diet, physical inactivity, stress, and certain medications.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
Symptoms can include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and headaches.
When should I consider medication for high blood sugar?
Medication may be necessary if lifestyle changes aren’t enough to manage your blood sugar levels effectively.
How often should I exercise to manage blood sugar?
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise each week, along with strength training at least twice a week.