What is Renal Cell Tumor?
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cancer, occurs when cells in the kidney begin to grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor. This condition can affect one or both kidneys and is most commonly diagnosed in adults.
Early detection is crucial, as kidney cancer can progress and spread to other parts of the body if not treated promptly.
Types of Kidney Cancer
The most prevalent type of kidney cancer is renal cell carcinoma (RCC), which accounts for about 85% of cases. RCC originates in the lining of the kidney’s tubules and can vary in appearance and behavior.
Another type, transitional cell carcinoma (TCC), starts in the renal pelvis, the area where urine collects before moving to the bladder, and can also affect the bladder itself. While less common, Wilms tumor primarily affects children, usually those between the ages of 3 and 4.
Additionally, collecting duct carcinoma is a rare and aggressive form of kidney cancer that develops in the collecting ducts of the kidney.
Risk Factors and Causes
Various factors can raise the likelihood of developing kidney cancer. Smoking is a significant risk factor, as tobacco use has been linked to a higher incidence of the disease. Obesity is another contributing factor, with excess body weight correlating with an increased risk.
Individuals with high blood pressure (hypertension) may also be at a greater risk. A family history of kidney cancer can elevate one’s susceptibility, particularly for those with certain genetic conditions like von Hippel-Lindau disease.
Furthermore, exposure to specific chemicals, such as asbestos or cadmium, has been associated with an increased risk of kidney cancer.
This comprehensive overview sheds light on kidney cancer, its various types, and the factors that may contribute to its development. c
Symptoms of Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer may not always present noticeable symptoms in its early stages, but as the disease progresses, various signs can emerge. Being aware of these symptoms is essential for early detection and prompt treatment.
Common Symptoms
The most common symptoms of kidney cancer include blood in the urine (hematuria), which may appear bright red or cola-colored. Other symptoms can include persistent lower back pain on one side, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and a noticeable lump or mass in the abdomen.
Additionally, individuals may experience changes in appetite, persistent fevers, or elevated blood pressure. It’s important to remember that these symptoms can also be associated with other conditions, so they should not be taken as a definitive diagnosis.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience any of the common symptoms mentioned above, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional. Seeking medical advice is especially important if you notice blood in your urine, unexplained weight loss, or persistent pain that does not improve.
Early diagnosis can significantly enhance treatment outcomes, so don’t hesitate to reach out to your doctor if you have concerns about your health.
This section highlights the importance of recognizing symptoms and knowing when to seek medical attention, which is vital for managing kidney cancer effectively. If you need further information or assistance, just let me know!
Diagnosing Kidney Cancer
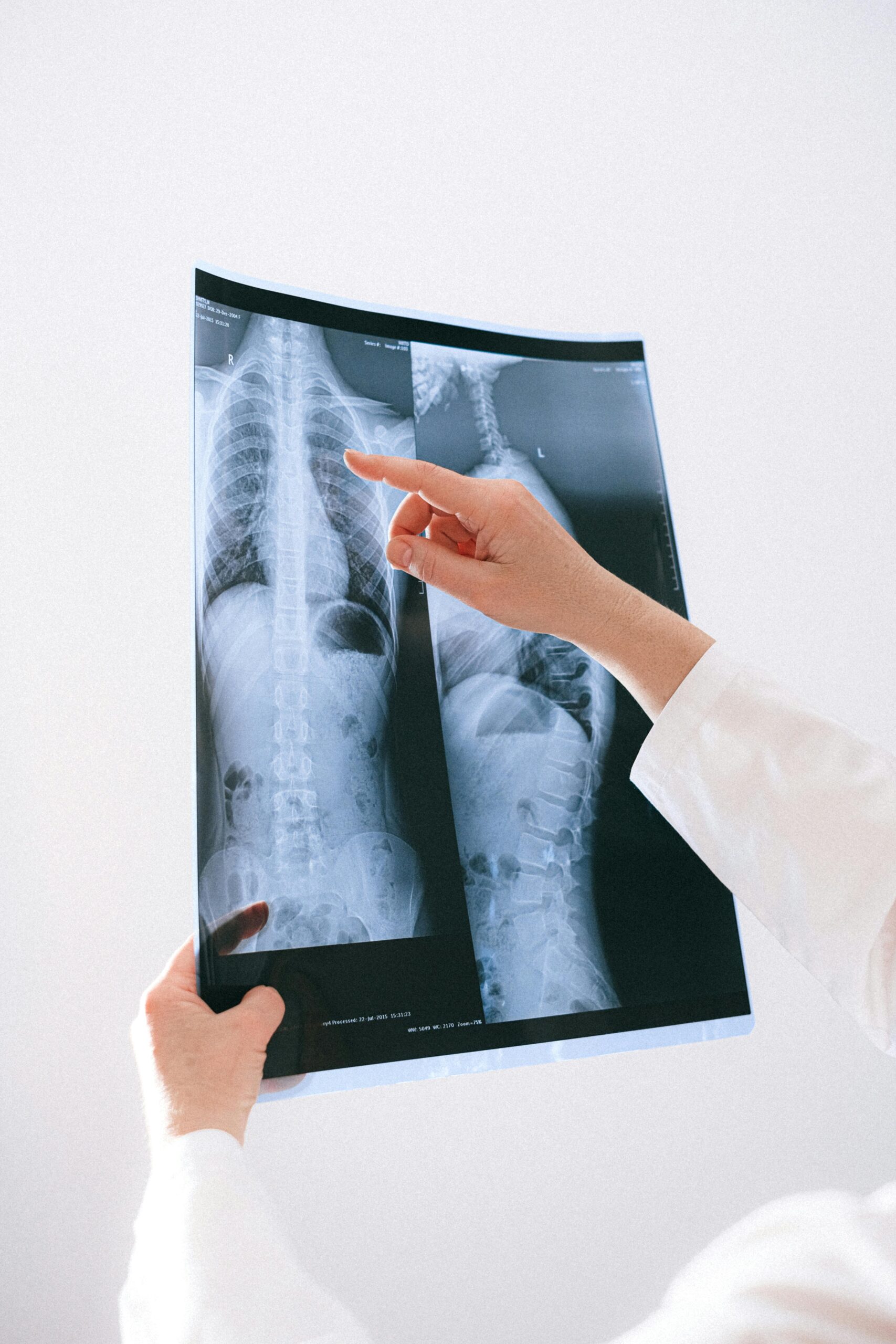
Diagnosing kidney cancer involves a series of steps, starting with a thorough evaluation of symptoms and medical history, followed by various diagnostic tests.
Early detection is critical for effective treatment, so understanding the diagnostic process is essential.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
The diagnosis of kidney cancer typically begins with imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans. These imaging techniques help visualize the kidneys and identify any abnormal growths.
If a suspicious mass is detected, a healthcare provider may recommend a biopsy, which involves taking a small sample of tissue from the tumor to examine for cancerous cells.
Blood tests may also be conducted to assess kidney function and detect any potential markers associated with cancer. Together, these tests provide a comprehensive view of the individual’s health and aid in confirming a diagnosis.
Staging Kidney Cancer
Once kidney cancer is diagnosed, it’s essential to determine its stage, which indicates how far the cancer has spread. Staging typically involves classifying the cancer using the TNM system: “T” for the size of the tumor, “N” for the involvement of lymph nodes, and “M” for metastasis, or spread to other parts of the body.
Staging helps guide treatment decisions and provides insight into the prognosis. The stages range from Stage I, where the tumor is small and localized, to Stage IV, where the cancer has spread to distant organs. Understanding the stage of the disease is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
This section outlines the critical steps in diagnosing kidney cancer, emphasizing the importance of early detection and accurate staging for effective management. If you need more details or have any questions, feel free to ask!
Treatment Options for Kidney Cancer
Treating kidney cancer involves several approaches, and the choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences. Here are the primary treatment options available for kidney cancer.
Surgery for Kidney Cancer
Surgery is often the primary treatment for kidney cancer, particularly in the early stages.
The most common surgical procedures include partial nephrectomy, where only the tumor and some surrounding tissue are removed, and radical nephrectomy, which involves the removal of the entire kidney along with nearby lymph nodes and tissue. In select cases, minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopic surgery, may be employed.
Surgery aims to remove as much of the cancer as possible and can significantly improve the chances of recovery.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy employs high-energy beams to focus on and eliminate cancer cells.
While it is not typically a first-line treatment for kidney cancer, it may be used in certain situations, such as when surgery is not an option, or to relieve symptoms caused by advanced disease. Radiation can also be utilized to shrink tumors before surgery or as palliative care to alleviate pain.
Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy
Chemotherapy is generally less effective for kidney cancer compared to other cancers, but it may be used in specific cases. More commonly, targeted therapy is employed, which focuses on specific molecules involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells.
These therapies can help inhibit tumor growth and are often used for advanced kidney cancer. Targeted therapies can have different mechanisms of action, such as blocking blood supply to tumors or interfering with the cancer cell’s ability to grow and divide.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy has emerged as a promising treatment option for kidney cancer. It works by enhancing the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively.
Checkpoint inhibitors, a type of immunotherapy, have shown significant success in treating advanced kidney cancer, offering patients new hope for improved outcomes.
This approach is particularly valuable for individuals who may not respond well to traditional treatments.
This section provides an overview of the various treatment options available for kidney cancer, highlighting the importance of personalized care based on individual patient needs. If you have further questions or need more information, feel free to ask!
Living with Kidney Cancer
Living with kidney cancer presents unique challenges, not only related to the physical aspects of the disease but also the emotional and psychological impacts. Understanding how to manage these challenges can enhance quality of life and support overall well-being.
Managing Side Effects
Treatment for kidney cancer, whether through surgery, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy, can lead to various side effects. Common side effects may include fatigue, nausea, changes in appetite, and pain. It’s crucial for patients to communicate openly with their healthcare team about any side effects they experience.
There are various strategies to help manage these effects, such as dietary adjustments, medications to alleviate nausea, and physical activity to combat fatigue. Supportive care services, including physical therapy and nutritional counseling, can also play a vital role in managing side effects and improving overall health.
Support and Resources
Navigating a kidney cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, which is why seeking support is essential. Many organizations provide valuable resources for patients and their families, including educational materials, support groups, and counseling services.
Connecting with others who are going through similar experiences can provide emotional relief and practical advice. Online forums and local support groups can foster a sense of community and help reduce feelings of isolation.
Additionally, healthcare providers can offer referrals to mental health professionals who specialize in oncology, ensuring that emotional well-being is prioritized alongside physical health.
This section emphasizes the importance of managing side effects and seeking support, which are crucial for maintaining a positive quality of life while living with kidney cancer. If you have any more questions or need further information, feel free to ask!
Prevention and Risk Reduction
While not all cases of kidney cancer can be prevented, certain lifestyle changes and proactive health measures can significantly reduce the risk. Understanding these strategies is vital for promoting kidney health and overall well-being.
Lifestyle Changes
Making specific lifestyle changes can help lower the risk of developing kidney cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can contribute to overall health and reduce cancer risk.
Regular physical activity is also essential; aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week can enhance physical fitness and support a healthy weight.
Additionally, avoiding tobacco products is crucial, as smoking is a significant risk factor for kidney cancer. Limiting alcohol consumption and staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water can further support kidney health.
Regular Check-ups and Screening
Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers are important for early detection and risk management. Although there are no standard screening tests specifically for kidney cancer in the general population, individuals with known risk factors—such as a family history of kidney cancer or certain genetic conditions—may benefit from more frequent monitoring.
Discussing personal risk factors with a healthcare provider can lead to tailored screening recommendations. Being proactive about health, including routine blood tests and imaging when necessary, can help identify potential issues before they become more serious.
This section highlights the importance of prevention and risk reduction strategies, focusing on lifestyle modifications and the value of regular medical check-ups. If you have any further questions or need more information, just let me know!
Conclusion
Kidney cancer is a serious condition that requires timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Understanding the types of kidney cancer, recognizing symptoms, and being aware of risk factors are crucial for early detection and effective management. Various treatment options, including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, offer hope for patients at different stages of the disease.
Living with kidney cancer poses unique challenges, but managing side effects and seeking support can significantly improve quality of life. Additionally, making lifestyle changes and staying vigilant through regular check-ups can help reduce the risk of developing kidney cancer.
FAQs
What are the survival rates for kidney cancer?
Survival rates vary by stage but are generally higher for early-stage diagnoses.
Can kidney cancer be prevented?
While not all cases can be prevented, lifestyle changes can reduce risk.
What are the main symptoms of kidney cancer?
Common symptoms include blood in urine, back pain, weight loss, and fatigue.
How is kidney cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests, biopsies, and blood tests.
What treatments are available for kidney cancer?
Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.