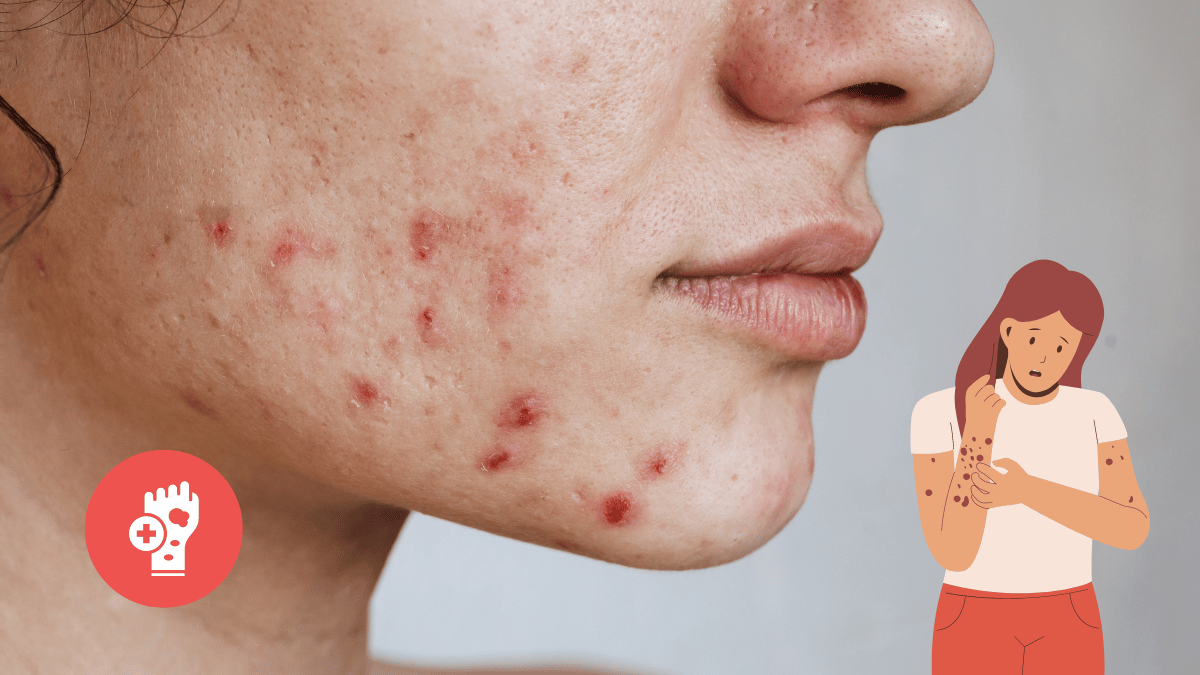
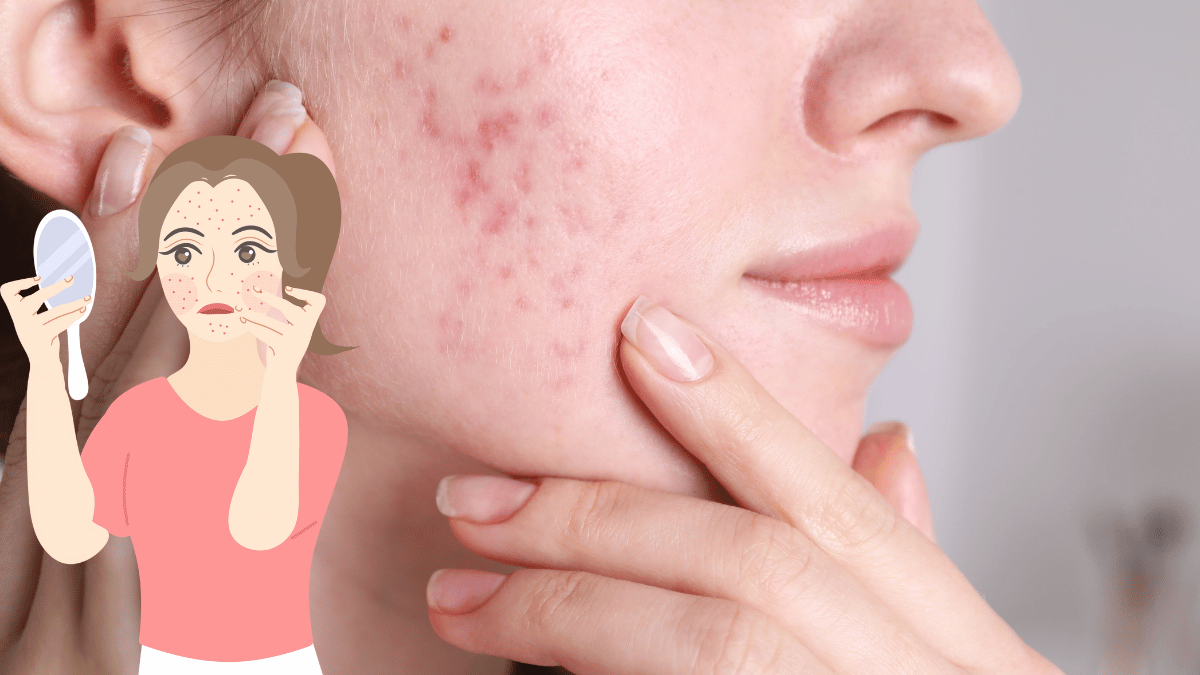
What Are Skin Diseases?
Definition of Skin Diseases
Skin diseases refer to a wide range of conditions that affect the skin, which is the body’s largest organ. These diseases can result in various symptoms, including rashes, lesions, and changes in skin color or texture.
They can be caused by multiple factors, such as infections (from bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites), allergic reactions to substances, genetic predispositions, or environmental irritants. Each skin disease has unique characteristics and can vary significantly in severity, duration, and impact on a person’s daily life.
Importance of Skin Health
Maintaining healthy skin is essential for overall well-being. The skin serves as a protective barrier, shielding the body from harmful environmental elements and pathogens. It also plays a crucial role in regulating body temperature and providing sensory feedback. Moreover, skin health can greatly influence a person’s self-esteem and mental health.
Conditions like acne or eczema can lead to emotional distress and social withdrawal, highlighting the importance of addressing skin issues promptly. Additionally, many skin diseases can signal underlying health problems, making it vital to monitor skin condition regularly and seek medical advice when necessary. Overall, prioritizing skin health not only enhances physical appearance but also supports overall health and quality of life.
Common Types of Skin Diseases
Acne
Acne is one of the most prevalent skin conditions, primarily affecting teenagers but also adults.Acne develops when hair follicles get blocked with oil and dead skin cells, which can result in pimples, blackheads, and cysts. Factors like hormonal fluctuations, stress, and certain medications can worsen the condition. While often associated with adolescence, it can persist into adulthood, making effective treatment essential for skin health and self-esteem.
Eczema
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic condition characterized by inflamed, itchy, and red patches of skin. It commonly affects children but can occur at any age. The exact cause is often unknown, but it may be linked to genetic factors and environmental triggers. Managing eczema typically involves moisturizing regularly, avoiding irritants, and using prescribed topical treatments to reduce inflammation and itching.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder that results in rapid skin cell turnover, leading to thick, scaly patches on the skin’s surface. These patches can be itchy and sometimes painful. The condition can affect any part of the body but is commonly found on the elbows, knees, and scalp. Psoriasis often has flare-ups and remissions, and while there is no cure, various treatments—including topical therapies, phototherapy, and systemic medications—can help manage symptoms.
Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes acne-like bumps. It often flares up in response to triggers such as sun exposure, stress, or certain foods. While there is no cure, treatments are available to help control symptoms and minimize flare-ups, including topical medications and lifestyle adjustments.
Skin Infections (e.g., Fungal, Bacterial)
Skin infections can arise from various pathogens, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Common bacterial infections include impetigo and cellulitis, while fungal infections like athlete’s foot and ringworm are also prevalent. Symptoms may vary but often include redness, swelling, and pain. Timely diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications and promote healing.
Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is a serious condition that arises from the uncontrolled growth of skin cells.The most prevalent forms include basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Risk factors include excessive sun exposure, a history of sunburns, and genetic predisposition. Early detection through regular skin checks and awareness of changes in moles or skin appearance is vital for effective treatment and better outcomes. Protective measures, such as using sunscreen and avoiding tanning beds, are essential for prevention.
Symptoms of Skin Diseases
General Symptoms to Watch For
Many skin diseases share common symptoms that can indicate an underlying issue. General symptoms to be aware of include:
- Redness or Inflammation: Areas of the skin may become red or swollen, signaling irritation or infection.
- Itching or Pain: Persistent itching or discomfort can indicate various skin conditions, often prompting further investigation.
- Dryness or Flakiness: Skin may appear dry, rough, or flaky, which can be associated with conditions like eczema or psoriasis.
- Rashes or Lesions: Unexplained rashes or lesions, whether raised, flat, or blistered, can indicate several skin disorders.
- Changes in Color: Dark or light spots or patches may develop, which could be benign or indicative of a more serious issue.
- Scaliness or Peeling: Areas of skin may become scaly or start to peel, often related to fungal infections or psoriasis.
Specific Symptoms by Disease
Different skin diseases manifest with distinct symptoms. Here are some specific indicators for common conditions:
- Acne: Characterized by pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and cysts, often accompanied by inflammation and scarring.
- Eczema: Symptoms include intense itching, red patches, and dry, cracked skin, often found on the elbows, knees, and face.
- Psoriasis: Notable for thick, silvery scales and red patches, which can be itchy and painful, commonly occurring on elbows, knees, and the scalp.
- Rosacea: Features facial redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes acne-like bumps, typically affecting the cheeks, nose, and forehead.
- Fungal Infections: Symptoms vary but may include red, itchy rashes, often with scaling and flaking, such as in athlete’s foot or ringworm.
- Skin Cancer: Symptoms include new growths, changes in existing moles (size, shape, color), and non-healing sores. Melanoma may appear as an irregularly shaped mole with varied colors.
Causes of Skin Diseases
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors are crucial in the development of many skin diseases. Conditions like psoriasis, eczema, and acne often have hereditary components, meaning individuals with a family history of these disorders are at a higher risk. Genetic variations can affect skin barrier function and immune responses, making some people more susceptible to certain conditions.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental triggers play a significant role in skin health. Factors such as UV radiation from the sun can cause damage, leading to conditions like sunburn and skin cancer.
Pollution and exposure to harsh chemicals can irritate the skin and exacerbate existing conditions. Seasonal changes, humidity, and temperature fluctuations can also influence skin health, triggering issues like dryness or flare-ups.
Lifestyle Influences
Lifestyle choices greatly affect skin health. Diet, stress levels, and skincare routines all play a part. Poor nutrition, lack of hydration, and insufficient sun protection can contribute to skin problems.
Additionally, habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can lead to premature aging and skin diseases. Regular exercise and stress management are vital for maintaining healthy skin and preventing various conditions.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
How Skin Diseases Are Diagnosed
Diagnosing skin diseases typically begins with a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. The process often involves a detailed physical examination of the skin, where the doctor inspects any rashes, lesions, or abnormalities present.
Alongside this, the physician will gather a thorough medical history, which includes inquiries about previous skin issues, family history of skin conditions, and any potential environmental or lifestyle triggers that may contribute to the current symptoms. In certain cases, specialized skin tests or biopsies might be conducted to provide more accurate diagnoses or to rule out other skin disorders.
If an allergic reaction is suspected, the doctor may recommend allergy testing to identify specific allergens that could be causing the skin condition. This multifaceted approach ensures that the diagnosis is accurate, paving the way for effective treatment.
Treatment Methods
Once a diagnosis has been established, the treatment for skin diseases varies widely depending on the specific condition and its severity. A common first line of treatment involves topical therapies, which include corticosteroids, moisturizers, and various medicated creams or ointments.
These treatments are designed to be applied directly to the affected areas, helping to reduce inflammation, soothe irritation, and promote healing. In cases where skin diseases are more severe or widespread, oral medications may be necessary.
These can range from antibiotics to address bacterial infections, antifungal medications for fungal issues, and systemic treatments like immunosuppressants for autoimmune conditions. Oral medications often provide a broader and more systemic approach to managing symptoms and addressing underlying causes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, skin diseases encompass a wide range of conditions that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding the types, causes, symptoms, and treatment options available is essential for effective management and prevention.
Early diagnosis is crucial, as it allows for timely intervention and can help mitigate potential complications. By recognizing general symptoms and seeking professional advice, individuals can address skin issues before they escalate.
Treatment often involves a combination of topical and oral medications, along with lifestyle changes that promote skin health. Maintaining a balanced diet, practicing good skincare routines, and managing stress are vital components of effective skin disease management. Moreover, awareness of environmental triggers and genetic predispositions can empower individuals to take proactive steps in safeguarding their skin.
FAQ
What are the most common skin diseases?
Common skin diseases include acne, eczema, psoriasis, rosacea, and skin infections.
How are skin diseases diagnosed?
Skin diseases are diagnosed through physical examinations, medical history, and sometimes skin tests or biopsies.
What treatments are available for skin diseases?
Treatments can include topical medications, oral medications, and lifestyle changes tailored to the specific condition.
Can skin diseases be prevented?
Many skin diseases can be prevented through proper skincare, sun protection, and avoiding known triggers.
When should I see a doctor about my skin?
You should see a doctor if you notice persistent or worsening symptoms, such as rashes, itching, or changes in moles.