Understanding Diabetes
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a long-term condition that disrupts the body’s ability to regulate glucose, a key energy source. In individuals with diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels, or it doesn’t effectively use the insulin that is produced.
This can lead to elevated blood sugar levels, which, if left unmanaged, can result in various health complications. Understanding diabetes is crucial for effective management and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Types of Diabetes: Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational
There are several types of diabetes, with Type 1 and Type 2 being the most common. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system wrongly targets and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This type is often diagnosed in children and young adults, and it requires lifelong insulin therapy for management.
On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes is the most prevalent form of the disease, frequently associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity and inactivity. In this case, the body either becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce enough of it. Management typically includes lifestyle modifications, such as improved diet and regular exercise, alongside oral medications or insulin if necessary.
Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy and typically disappears after delivery. However, it poses risks for both the mother and child, potentially leading to the development of Type 2 diabetes later in life. Managing gestational diabetes involves careful monitoring of blood sugar levels, dietary adjustments, and sometimes medication to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Importance of Diabetes Management
Why Managing Diabetes is Crucial
Managing diabetes effectively is vital for maintaining overall health and well-being. Proper diabetes management helps regulate blood sugar levels, which in turn reduces the risk of serious complications. When blood sugar is well-controlled, individuals can lead more active and fulfilling lives.
It allows them to prevent symptoms like fatigue, frequent urination, and excessive thirst, which can significantly impact daily activities. Moreover, good management can enhance emotional well-being, reducing anxiety and stress often associated with living with a chronic condition.
The Risks of Poor Diabetes Control
Neglecting diabetes management can lead to a host of serious health complications. Prolonged high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, nerves, and organs, resulting in conditions such as heart disease, kidney failure, and vision problems, including diabetic retinopathy.
Additionally, poorly controlled diabetes can increase the risk of infections and slow the healing process for wounds. In extreme cases, it may lead to diabetes-related emergencies, such as diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state, which can be life-threatening.
Understanding these risks underscores the importance of consistent and proactive diabetes management to ensure a healthier future.
Key Strategies for Diabetes Management
Healthy Eating Habits
Developing healthy eating habits is fundamental to managing diabetes effectively. A balanced diet helps regulate blood sugar levels and can prevent complications associated with the condition.
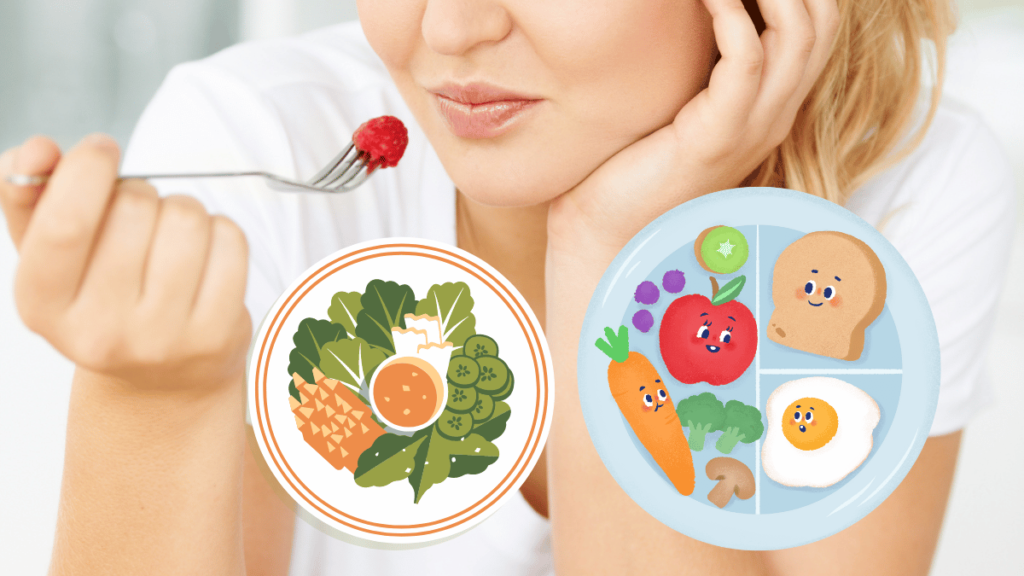
Creating a Balanced Meal Plan
A balanced meal plan includes a variety of foods, focusing on whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Portion control is essential, as it helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. Incorporating foods with a low glycemic index can also be beneficial, as they cause a slower rise in blood sugar. Planning meals in advance can simplify choices and help avoid unhealthy options.
Understanding Carbohydrate Counting

Carbohydrate counting is a fundamental approach for managing diabetes effectively. By tracking carbohydrate intake, individuals can make informed decisions about their meals, helping to maintain balanced blood sugar levels.
It involves understanding how different foods affect blood glucose and knowing how to adjust insulin doses or medications accordingly. This approach provides flexibility in meal planning while keeping blood sugar within target ranges.
Medications and Treatments
Common Medications for Diabetes
Managing diabetes often involves various medications tailored to individual needs. For those with Type 2 diabetes, oral medications such as metformin are commonly prescribed to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose production in the liver.
Other classes of medications may include sulfonylureas, which stimulate insulin release, and SGLT2 inhibitors, which help the kidneys remove excess glucose through urine.
Additionally, GLP-1 receptor agonists can aid in appetite control and weight management, providing a comprehensive approach to treatment. Each medication has its specific benefits and potential side effects, making it essential for individuals to work closely with their healthcare providers to find the best regimen.
Insulin Therapy Explained
Insulin therapy is crucial for those with Type 1 diabetes and may also be necessary for some individuals with Type 2 diabetes when oral medications are insufficient. Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the uptake of glucose into cells for energy.
There are various types of insulin, including rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting, each designed to meet different needs throughout the day.
Individuals using insulin therapy typically learn how to administer it via injections or insulin pumps, and they must regularly monitor their blood sugar levels to adjust dosages accordingly.
Education on recognizing signs of hypo- and hyperglycemia is also vital, as it empowers individuals to manage their condition effectively and maintain stable blood sugar levels. Overall, insulin therapy plays a fundamental role in the comprehensive management of diabetes, allowing individuals to lead healthier lives.
Conclusion
Effective diabetes management is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing complications associated with the condition. By adopting healthy eating habits, incorporating regular physical activity, and utilizing appropriate medications, individuals can take significant steps toward controlling their blood sugar levels.
Understanding the different types of diabetes and the importance of personalized treatment plans empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
As diabetes management is a continuous journey, staying educated and proactive is key. By seeking support from healthcare professionals, engaging in community resources, and utilizing available tools, individuals can enhance their quality of life and thrive despite the challenges of diabetes. Taking charge of your health today can lead to a healthier tomorrow, enabling you to live a fulfilling and active life.
FAQs
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes glucose.
What are the main types of diabetes?
The main types are Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes.
Why is managing diabetes important?
Proper management helps prevent serious health complications and improves quality of life.
What are common medications for diabetes?
Common medications include metformin, sulfonylureas, and insulin.
How does insulin therapy work?
Insulin therapy provides the hormone needed to regulate blood sugar levels, often via injections or pumps.